When Food Allergies and the Environment Collide
Presented by Dr. Chris D. Meletis, ND
Allergic signs and symptoms present when susceptibility is heightened or total burden is reached and the threshold (body tolerance) is exceeded. At this juncture inflammatory and allergic cascades as innate defense mechanisms are activated leading to the suffering and affliction attributed to allergies and intolerance. In this webinar, we review clinical pearls and research essential for helping liberate patients afflicted with an overwhelmed immune response.
Takeaway Points
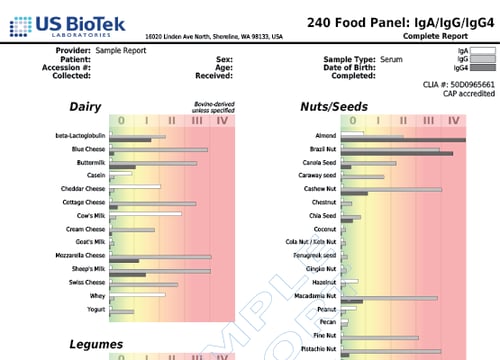
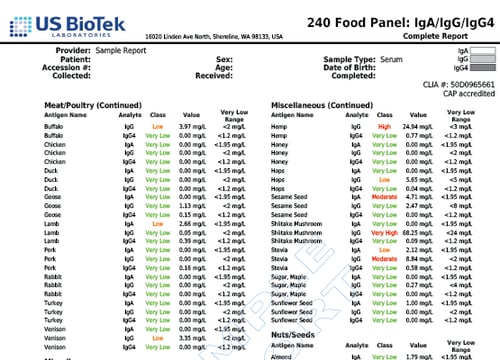
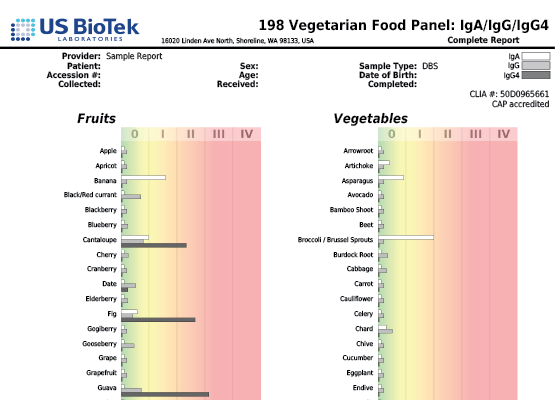
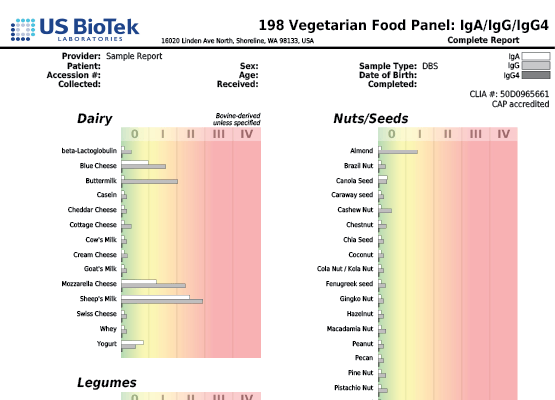
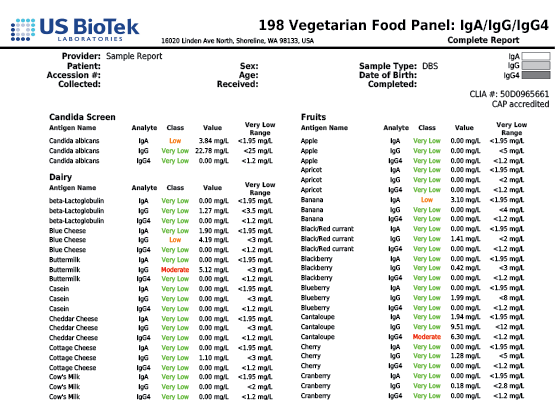
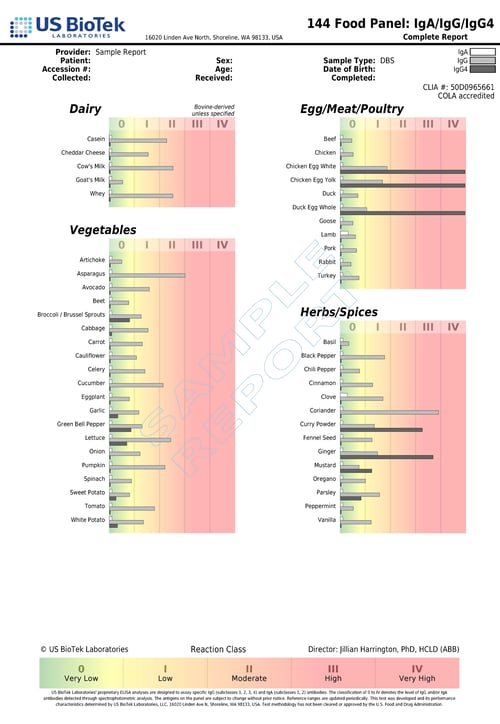
- Cross-reactivity can be seen in people who are allergic to pollen and also have allergy symptoms when exposed to certain food groups.
- In adults, up to 60 percent of all food allergic reactions occur because of cross-reactions between food and pollen.
- Birch pollen cross-reacts with hazelnuts, apples, celery, carrot and soy.
- About 50 to 60 percent of people who are allergic to latex also have "latex-fruit syndrome," where they develop adverse reactions after consuming cross-reacting vegetables and fruits including bananas, avocados, chestnuts, kiwis, chickpeas and bell peppers.
- Pollen from olive trees, ragweed and grasses also cross-reacts with a variety of food.
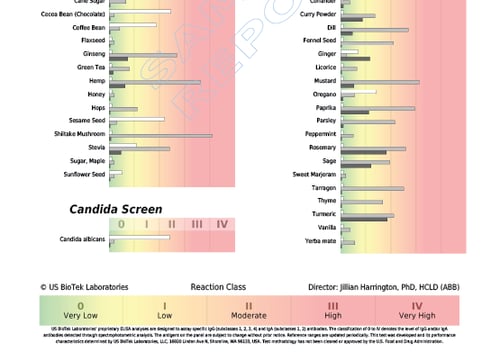
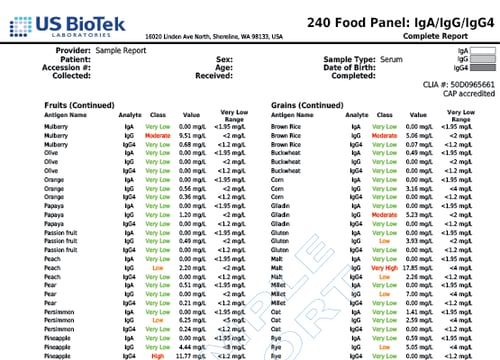
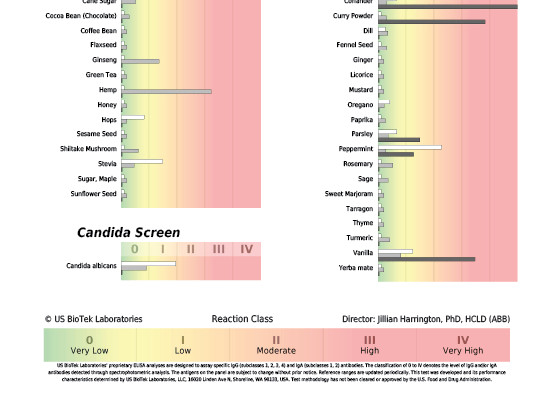
- Non-pollen related cross-reactions include Candida's association with yeast and gluten-containing foods cross-reacting with coffee, dairy, oats and yeast.